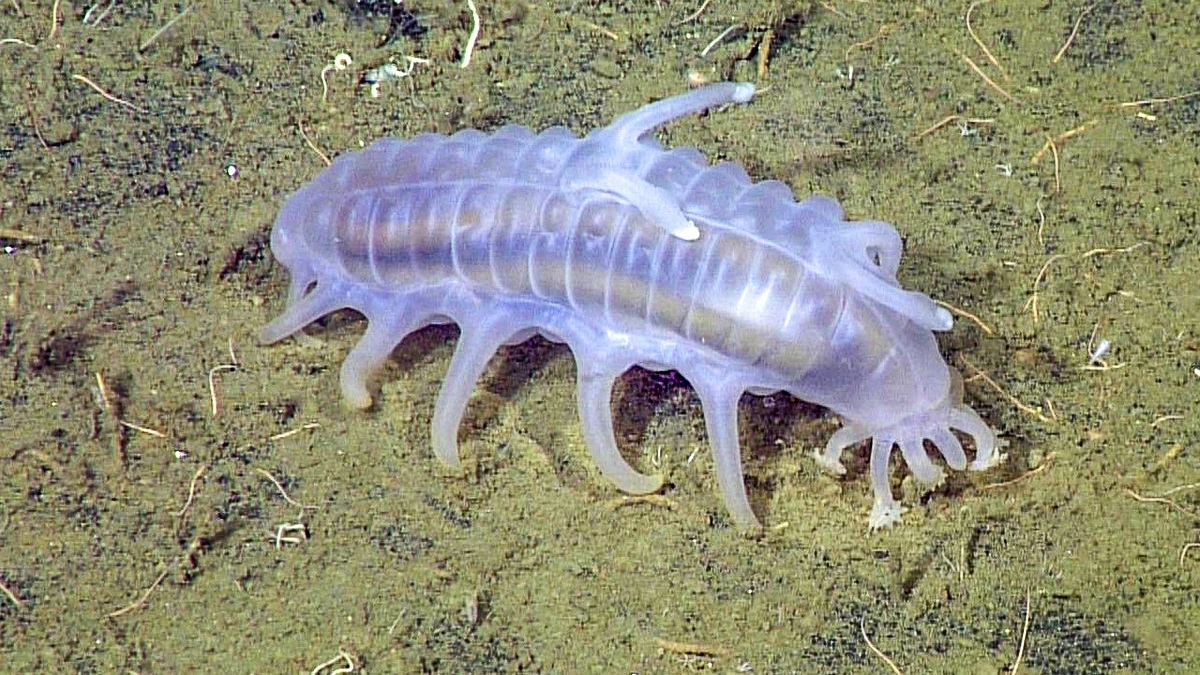
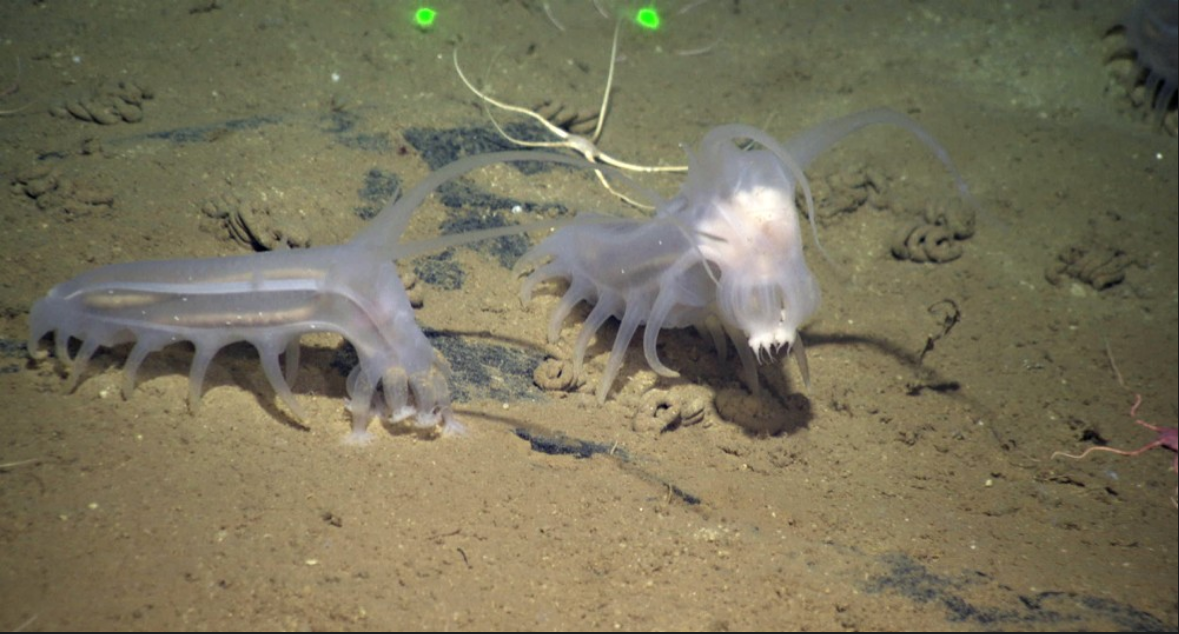
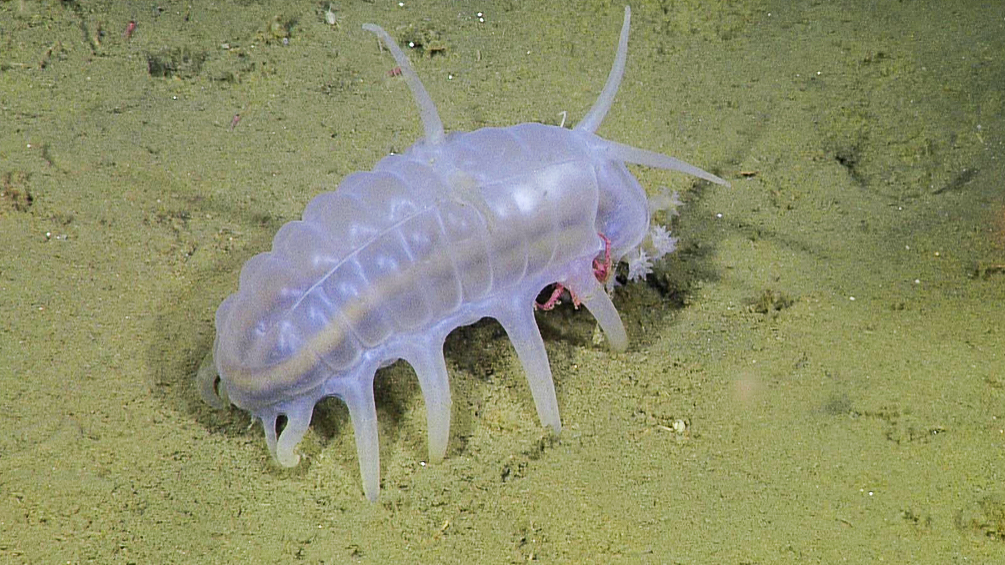
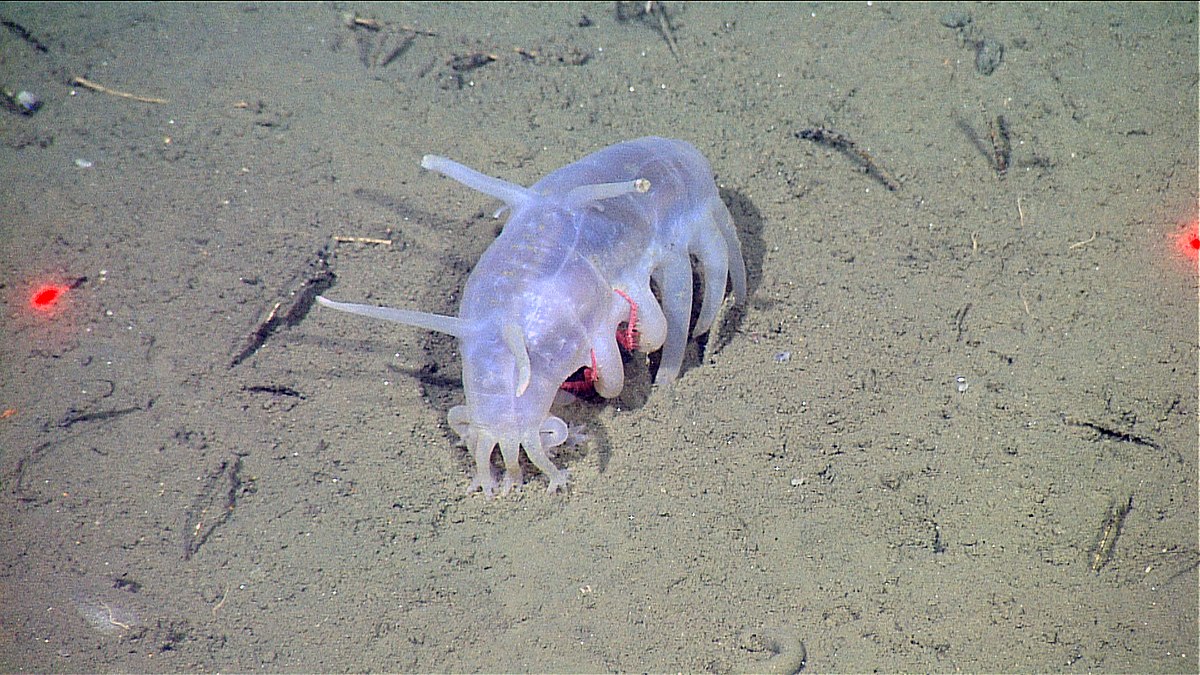
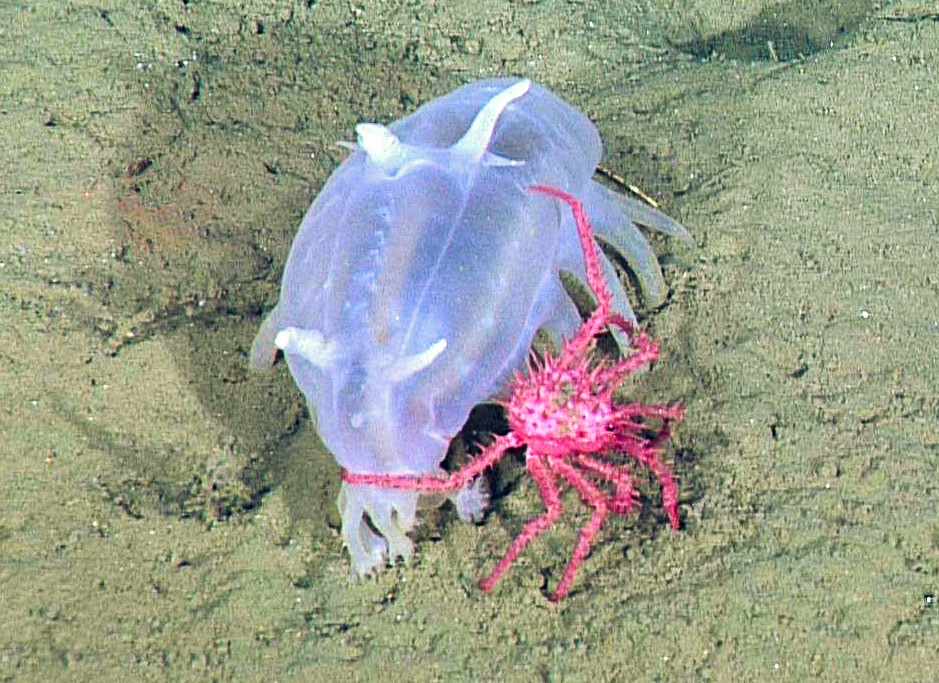
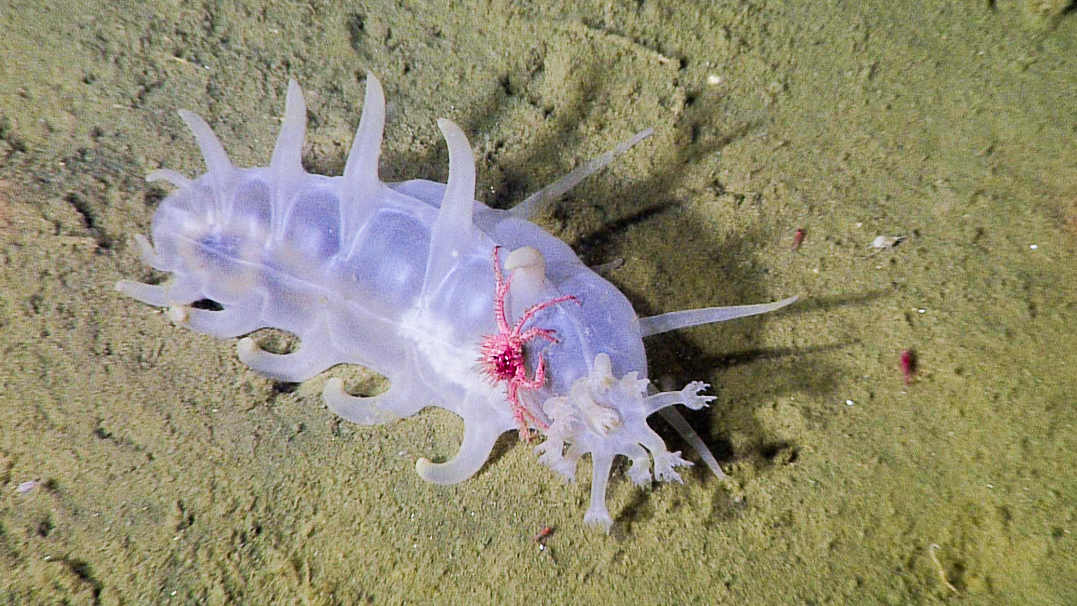
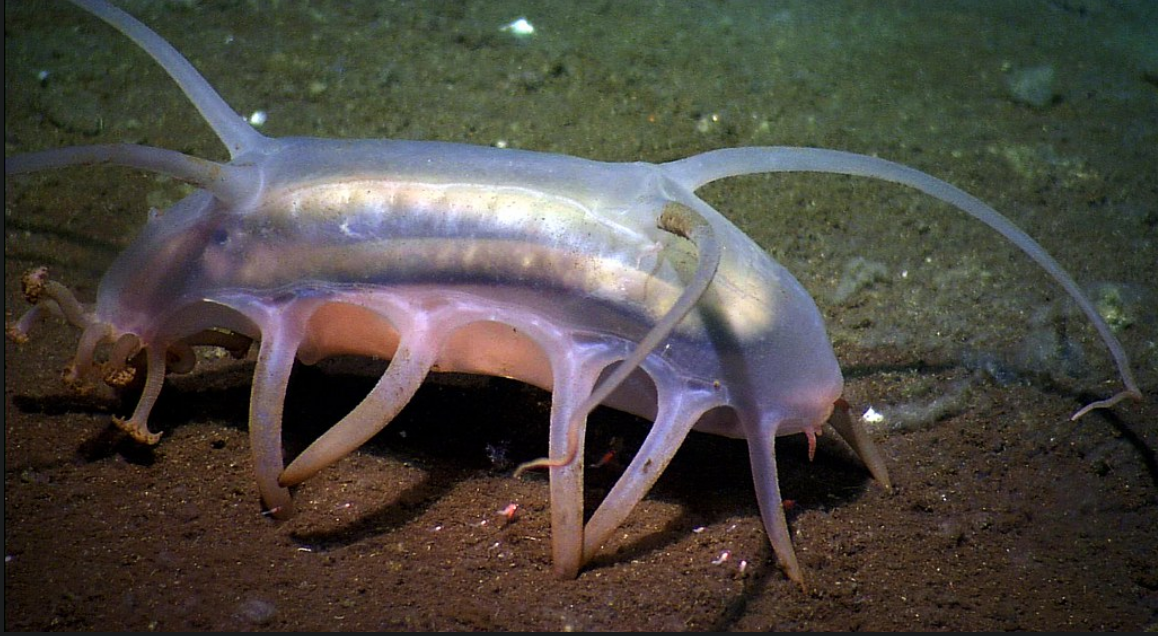
-Leeches are found all across the world, except Antarctica, so far around 700 species of leech have been described. Approximately 100 are marine, 480 freshwater and the remainder are terrestrial different species…. All of these are divided into 2 major infraclasses
-
Euhirudinea: the 'true' leeches – marine, freshwater and terrestrial – which have suckers at both ends and lack chaetae (bristles)
-
Acanthobdellida: a small northern hemisphere infraclass ectoparasitic on salmoniid fish, which lack an anterior sucker and retain chaetae.
The Euhirudinea is further divided into two orders:
-
Rhynchobdellida: jawless marine and freshwater leeches with a protrusible proboscis and true vascular system
-
Arynchobdellida: jawed and jawless freshwater and terrestrial leeches with a non-protrusible muscular pharynx and a haemo-coelomic system. source

Above image from here
-Leeches are segmented parasitic or predatory worms, and are closely related to earthworms
-They have suckers at both ends of their bodies and use them to travel around by ‘looping’ or ‘crawling.’ Some species can also swim like an eel

Above image by Chiswick Chap via wikipedia
-All leeches are hermaphrodites, although they prefer to find a mate to exchange sperm packets with…..
-They can live in both fresh and salt water, and there are some which are terrestrial, living on the ground or on low growing plants waiting for a meal to brush past
-Some species can even survive extremely dry conditions by burrowing into the soil where they can stay without any water. Their bodies contract, becoming dry and rigid, but within 10 minutes of water contact they emerge, ready to go!
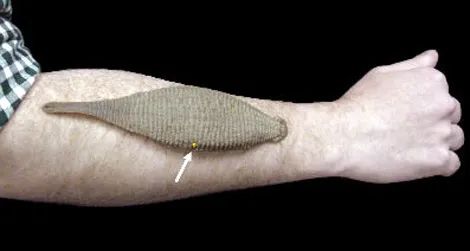
-The most famous type of leech is probably the European medicinal leech (Hirudo medicinalis), which was used extensively in the past (the first recorded case being Ancient Egypt 3500 years ago). Its populations in the wild have dropped significantly due to over exploitation for the medical industry
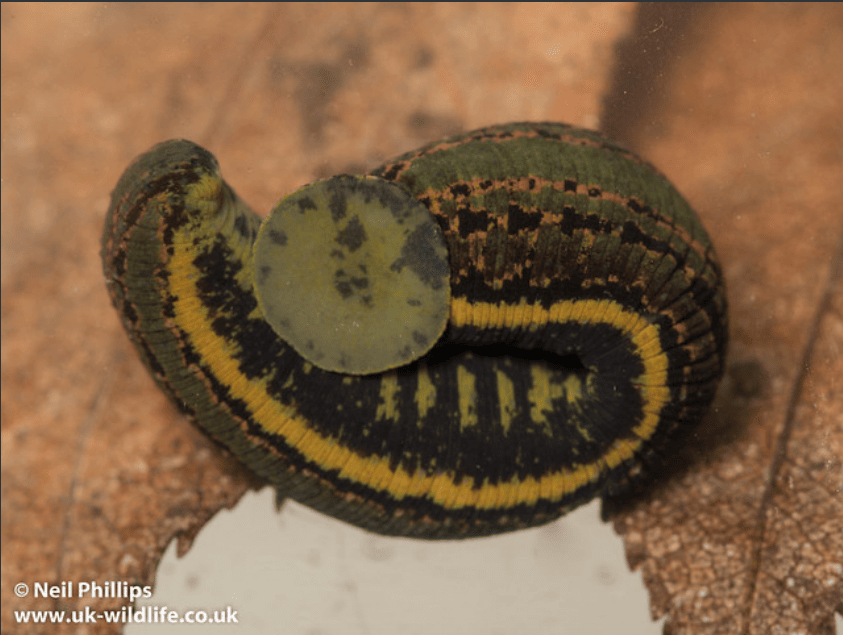

Photo by Neil Phillips
-Manchester Royal Infirmary used 50,000 leeches in one year in 1831, but use of the medicinal leech started to decline during the late 19th century. However, since the 1970’s they have made a comeback due to their use in micro surgery. Their anti coagulant saliva allows blood to keep flowing, and wounds to stay open during reattachment and reconstructive surgery!
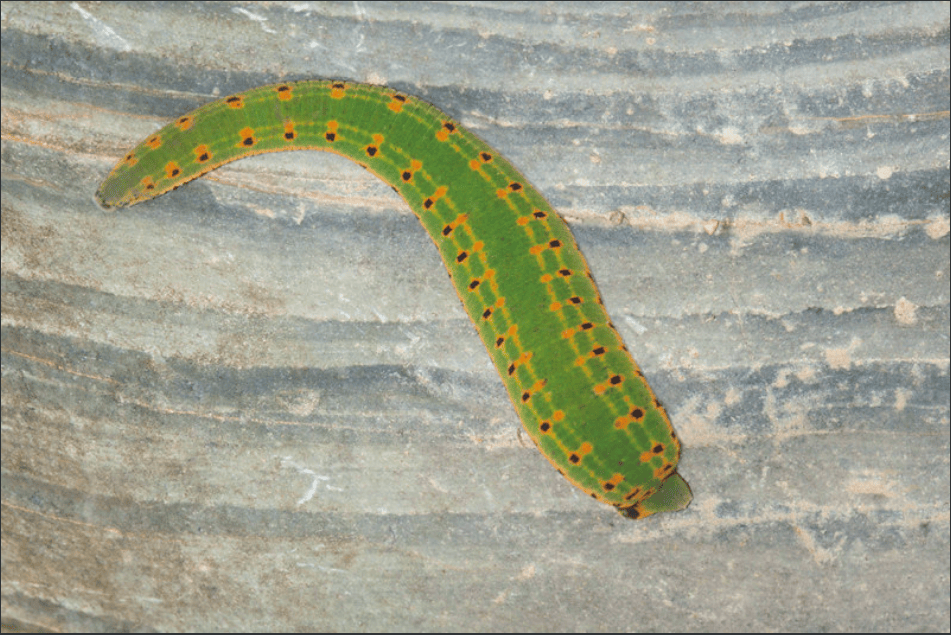

Photo by Armando Caldas
-Hirudo medicinalis are ‘jawed’ leeches (Gnathobdellida). They have 3 jaws resembling rotary saws which have around 100 sharp edges used to incise the host which leaves a Y shape wound on the skin. They are so tiny their bite is virtually painless. Blood suckers are only one type of leech though...
-Other species of jawed leeches can have between 1 and 3 jaws. Detrivorous species use their jaws for chewing and swallowing soft food particles, whilst the carnivores use them to cut a hole in the body walls of invertebrate prey (molluscs, worms, insect larvae), in order to suck out the soft innards.
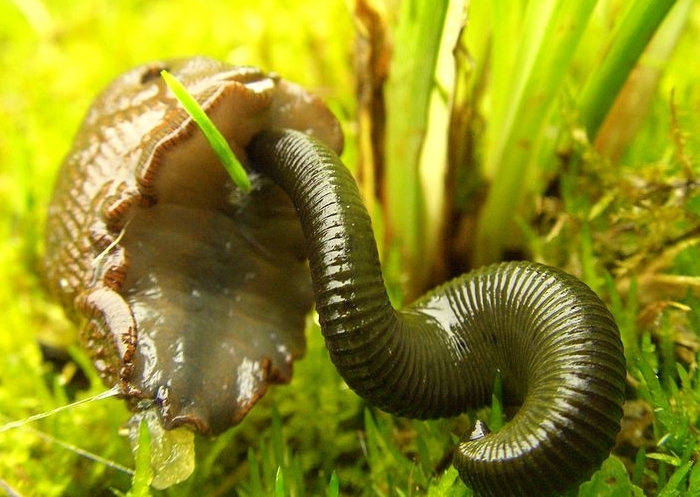

Photo by Manuel Krueger-Krusche
-The largest fresh water leech in the world is Haementeria ghilianii, (the Amazon giant leech) which can grow up to 450mm long and 100mm wide. One end of the leech contains its head, and the other the proboscis, which is 10cm long and like a hypodermic needle. It is capable of feeding on humans, rabbits, cattle and horses and a report from 1899 claims it could feed in such numbers that it could kill cattle and birds
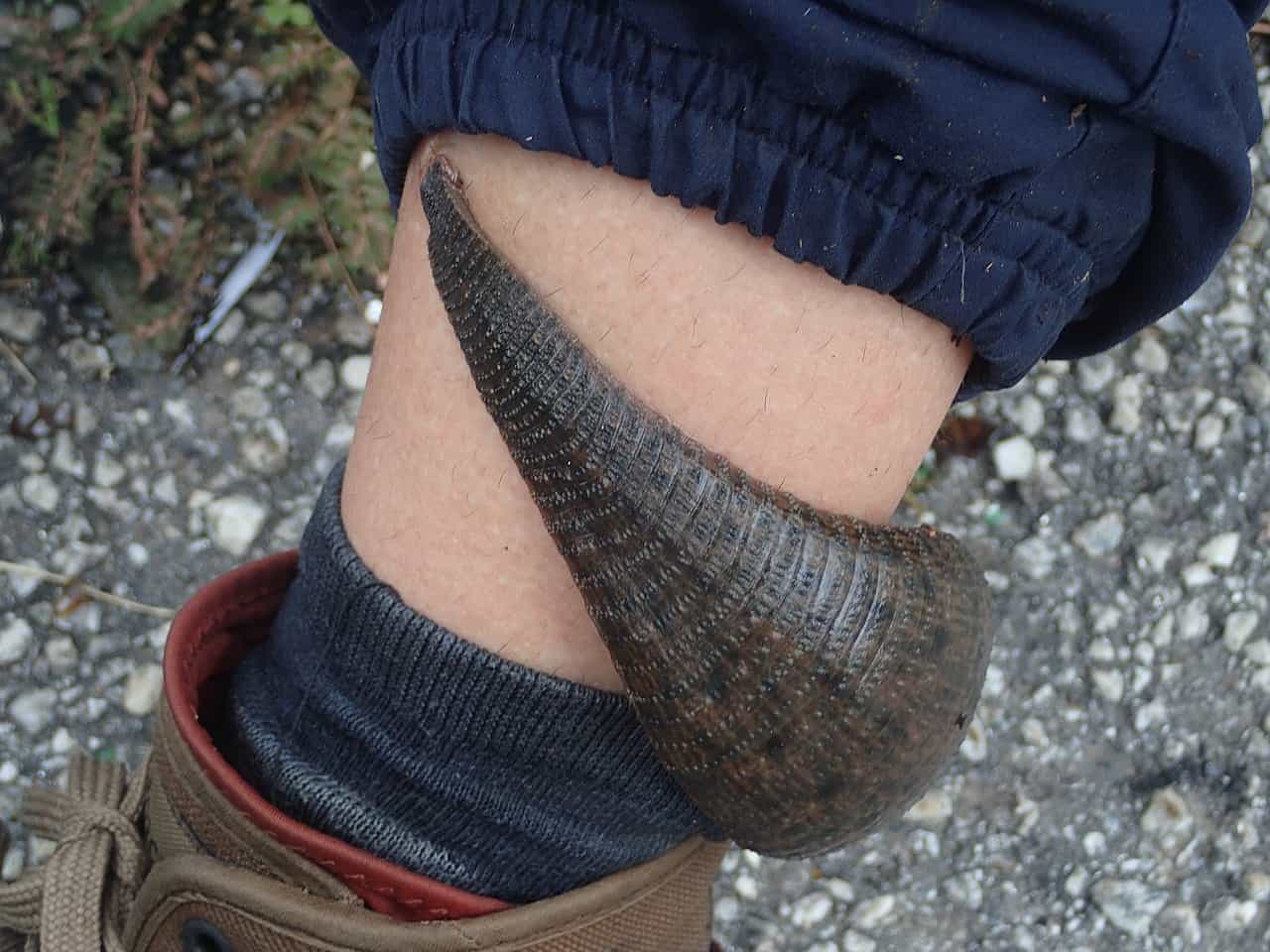

Photo by Anonyme973
-Its male reproductive parts can weigh 3-5 grams, and the female parts weigh in at 10 grams, they are capable of producing egg clutches ranging from 60 to 500 eggs
-It was thought to be extinct in 1893, however during the 1970s Dr Roy Sawyer discovered 2 specimens in a pond in French Guiana. One of these was transferred to the UC Berkeley where it was part of a ‘breeding’ program. Named ‘Grandma Moses’ it managed to produce 750 offspring over 3 years, and helped to bring the Amazon Giant Leech back from the brink of extinction
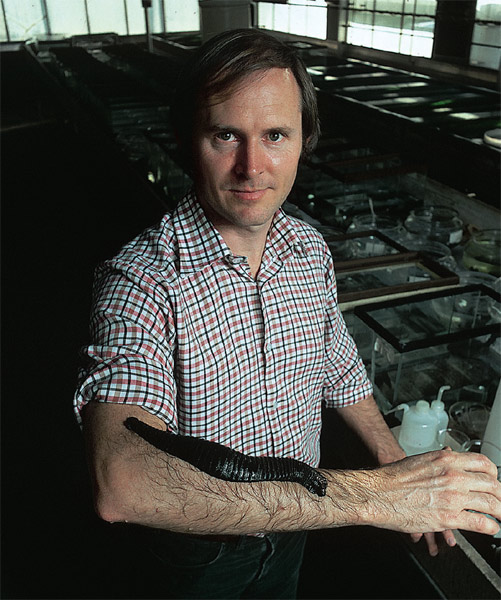

Dr. Roy Sawyer and friend photographed by Timothy Branning
-When it died, ‘Grandma Moses’ was given to the Smithsonian National Invertebrate Collection where it still resides preserved in alcohol!
The Grandma Moses leech
-A small minority of leech species have no jaws or teeth (these are the worm leeches or Pharyngobdellida). Instead they swallow their prey, usually small invertebrates, whole!
-The Kinabalu giant red leech (Mimobdella buettikoferi) is probably one of the longest leeches, growing over 50cm.
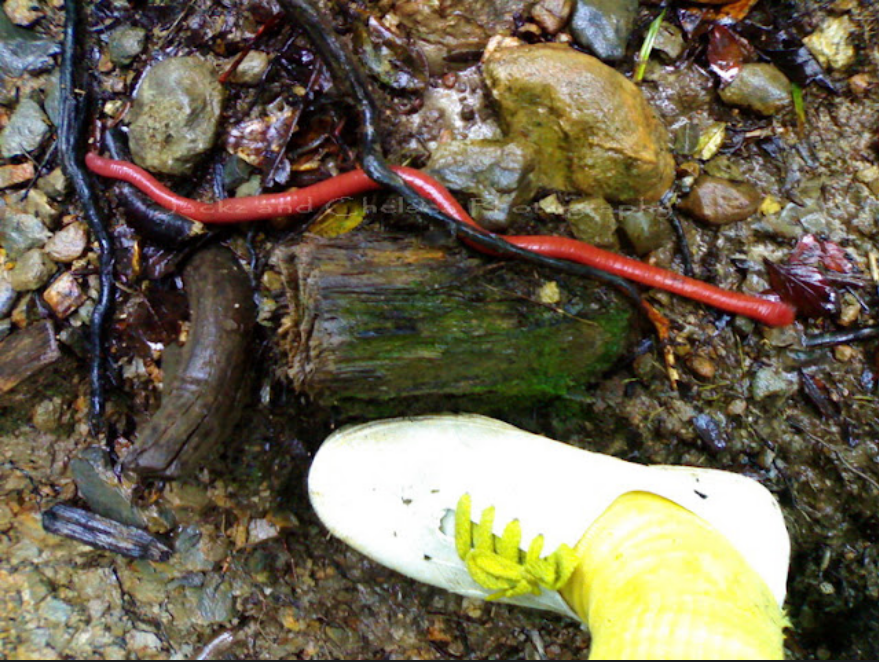

Above photo from here
-It lives only on Mt Kinabalu, Borneo and feeds on an equal giant prey, the Kinabalu giant earthworm (Pheretima darnleiensis)
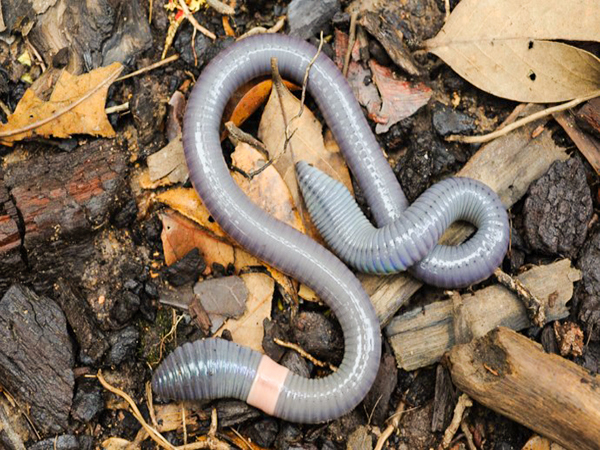

Kinabalu giant earthworm, Photo by Chien Lee

Kinabalu giant earthworm, Photo by Ivan Kwan
-It lives among the leaf litter and soil, and both leech and worm are usually seen during or after a downpour….
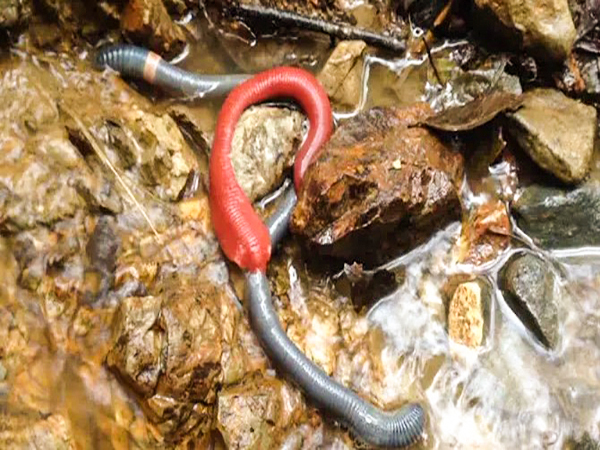

Found here
A hungry leech is very responsive to light and mechanical stimuli. It tends to change position frequently, and explore by head movement and body waving. It also assumes an alert posture, extending to full length and remaining motionless. This is thought to maximise the function of the sensory structures in the skin. source
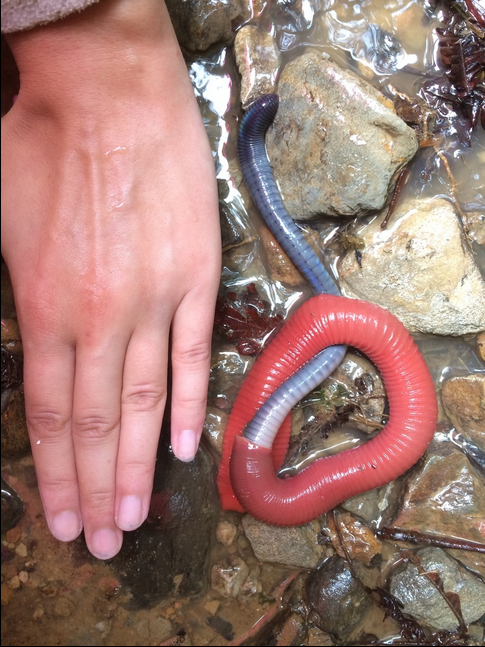

Photo from here
-When it finds a worm it begins to grope towards an end, then it begins to suck…..
Here is a delightful film of just that!
Also on youtube
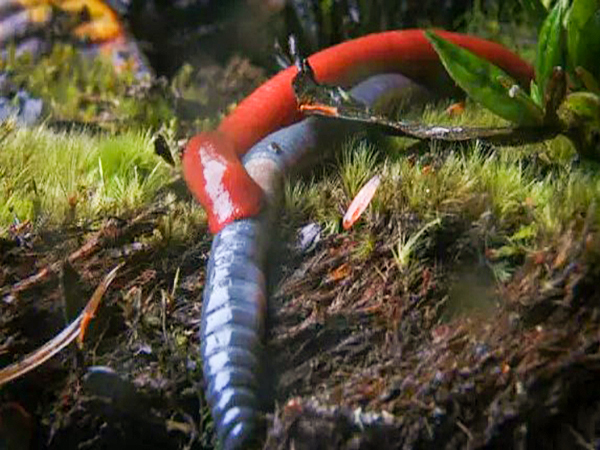
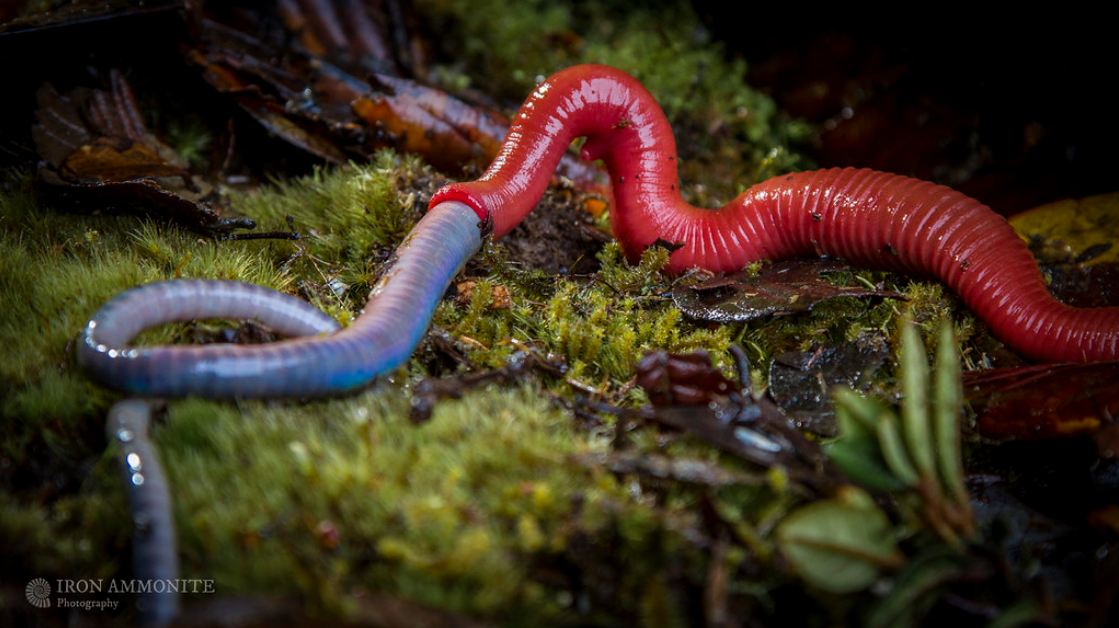


Above photos by Paul Williams
-Almost all leeches have at least one pair of tiny eyes, however some can have up to 16, these are arranged in patterns although their vision may only be able to detect light and dark.

Photo by Paul
-Glossiphoniid leeches demonstrate exceptional parental care for their offspring, which is the most highly developed for the annelids (the worm species). They produce a membranous bag in which they keep their eggs, this is carried on the underside of their bodies. When the young hatch they attach onto their parents belly (but not with a feeding bite) and the parent carries them to their first meal!

Above photo by Maralee Joos

Above photo by Duncan Cooke

Above photo by Duncan Cooke
Helobdella, which have a world-wide distribution, display the most highly developed parental care system: they not only protect but also feed the young they carry. This results in the young being much larger when they leave the parent and, presumably, in higher subsequent survival. source

Above photo by Dick Todd
-Leeches are quite hardy, some can survive in low oxygen environments, others at low ocean depth such as….
Bathybdella sawyeri occurs at 2447–2623 m depth at the Galápagos Rift and the Southeast Pacific Rise and Galatheabdella bruuni has been found at depths of 3880–4400 m in the Tasman Sea (Richardson and Meyer, 1973; Burreson, 1981; Burreson and Segonzac, 2006). However, the leech that occurs at the greatest depth is Johanssonia extrema described by Utevsky et al. (2019) that was collected at a depth of 8728.8 m in the Kuril-Kamchatka Trench. Occurring at that depth, J. extrema withstands pressure that is over 870 times greater than that at sea level. source
-Some species have evolved to live within the extreme dark of caves, others to withstand the extreme cold of arctic waters, one lives in waters of high alkalinity with the addition of arsenic at levels >110mg/L
Members of Praobdellidae are characterized by feeding primarily from mucous membranes [mouth, throat, nasal passages, and under the eyelids] particularly of mammals, but also from the skin of amphibians. This behavior is considered equally unnerving by both academic and public audiences. source
-A backpacker returning from Vietnam discovered she had also brought home a leech passenger that was attached inside her nostril "At one point, I could feel him up at my eyebrow," she said. It was removed at Liverpool Hospital, before it could reach her brain…. She than kept the leech named ‘Mr Curly’ as a pet…. delightful!
-One other leech has evolved to live in another type of orifice...a hippos anus!
…...Placobdelloides jaegerskioeldi inhabits one of the most extreme environments of all of the leeches that invade orifices, the rectum of the hippopotamus (Oosthuizen and Davies, 1994). Adult P. jaegerskioeldi have papilla-bearing tubercules that are postulated to provide traction against the anal-wall of the hippopotamus (Oosthuizen and Davies, 1994). This species is also one of the few glossiphoniid leeches that can actively swim and swims (even upstream) to its hippopotamus host (Oosthuizen and Davies, 1994). source
As always, I’m not and expert I just like finding and sharing fun things I find on the internet. Any mistakes or errors, let me know in the comments and I’ll edit my post!
All information via wikipedia-
Leech
Giant Amazon Leech
Medicinal Leech
Kinabalu Giant Leech
Glossiphoniidae
Except these-
Bogleech
Smithsonian Magazine
Australian Museum
buzzfeed
Leeches in the extreme: Morphological, physiological, and behavioral adaptations to inhospitable habitats
mentalfloss
The Evolution of Parental Care in Freshwater Leeches